New-era TV: let’s talk about what is CTV and its advantage
- Author:: Lizaveta Zhuk
From the way users network, to the way users get their news, they are slowly but surely moving everything online — and TV is no exception. With developing technologies and the Internet proliferation, users watch TV content in a new way on the Connected TV. And it opens new opportunities for brands in reaching users and scaling ad campaigns.

Source: Marketing Dive, Leichtman Research Group
How does it work? Let’s learn in our new article.
What is connected TV advertising?
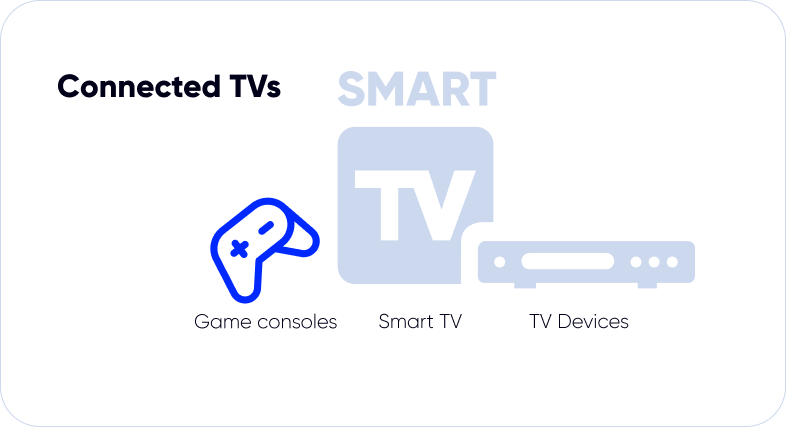
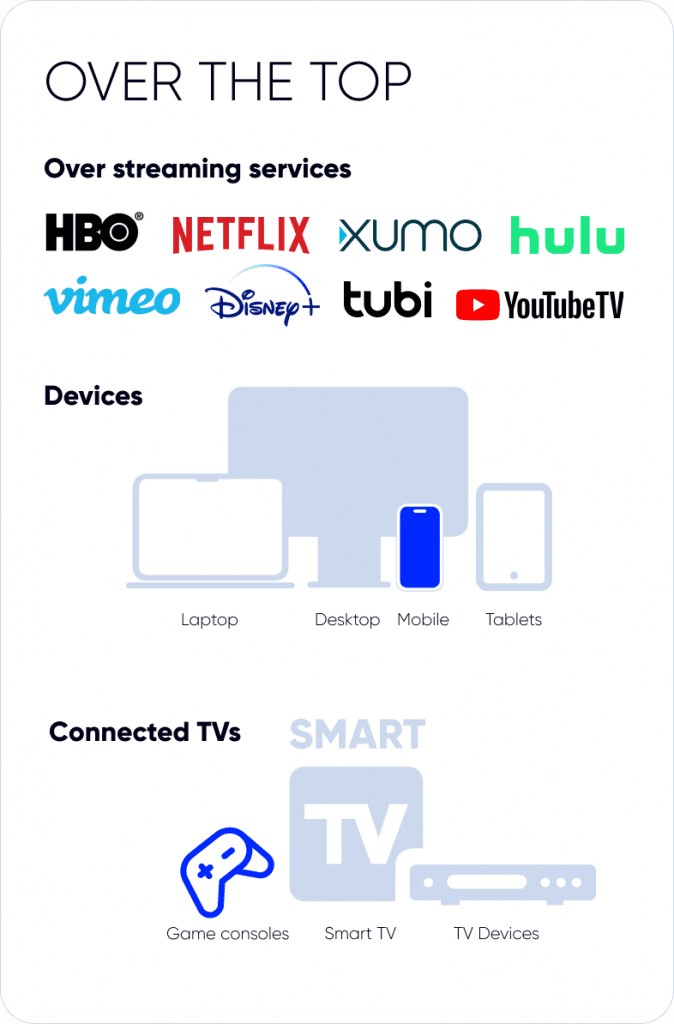
Connected TV ads is a practise of delivering advertising through any content streamed from a video provider via a device connected to the internet including:
- Smart TV is a TV with a connection to the Internet. Allows you to connect to various streaming platforms or services by installing certain apps or watching video content via a browser app.
- Game consoles are new era game consoles connected to the TV screen and internet streaming services (Nintendo, Playstation, and so on).
- Set-Top-Box (TV box) is a cable box that connects a TV to the internet and gives access to streaming services.
Simply put, it’s a new type of TV ads but in a new way — more efficient and more technological. The first version of the familiar television we used to watch was invented almost 100 years ago, and doesn’t fit the modern advertising world: there are no targeting options and the same ads are watched by the wide audience of the channel without considering any user data, even demographic and interest.
CTV allows targeting narrow segmental circles, which results in personalized and relevant advertising that meets the interests of a specific audience, does not irritate it, and, as a result, most often leads to the performance of targeted action. For marketers, it can help achieve the following:
- increase brand awareness;
- drive outreach;
- build demand on particular products or services;
- drive user’s engagement and so on.

Source: Innovid | Digiday
CTV and OTT: how are they different?
These two terms are easy to confuse. Their meanings are similar and differ precisely in the technical component.
OTT is a technology of providing video over the Internet to all devices. The abbreviation OTT means “over the top”, which means that content is provided not by cable or network but by the Internet. Content that initially made it onto TV screens via broadcast, cable, or satellite became available online. In the case of Connected TV, it is more about devices for displaying video such as Smart TV, game consoles, etc. This way, CTV represents the tech core for OOT streaming content.
Let’s give one example. If a user watches a HBO movie on his or her tablets, it means that he or she is streaming OTT content. But if a user decides to watch an HBO movie through a physical device that is connected to his or her TV, the user will watch OTT content over CTV.
Advertising opportunities: ad formats
There are some common types of advertising formats for Connected TV that advertisers can use:
In-stream video ads. It’s the most impressive ad format. Video ads are usually 15-30 seconds duration and can be pre-roll, mid-roll and post-roll depending on when advertisement would appear before, middle or after the main streaming content respectively.
Pros:
- quickly engage the audience and retain attention as they cannot miss them
- users are already familiar with the format and like it more than live ads if it’s relevant to their interest
- may increase purchase intent and drive conversion — nearly 8 out of every 10 users have purchased a piece of software or app after having watched the brand’s video.
Cons:
- limitation of video length: it shouldn’t be longer than 60 seconds
- ads may appear alongside several other ads
Interactive video ads. It is a type of ads that come in various forms such as a QR code, an overlay while streaming content and others that encourage users to interact with ads and take particular action. For example, screen QR code.
Pros:
- drive users engagement due to interactive component
- may deliver more conversions and outcomes that brands look to achieve
- high viewability and so on
Cons:
- not all platforms support this ad format
- often require more technical and designed development and opportunities
- may be more expensive than other ad formats
Display ads (banner). Connected TV is not only for video content, you can also target banner ads to your target audience on a big screen of streaming devices. It is usually smaller in size and does not take over too much screen, and may display on the homescreen of the CTV platform or as an overlay while a user watches content.
Pros:
- no limitations in length of an advertisement
- reach a wide audience
Cons:
- it doesn’t occupy the entire screen so requires short message and call to action
- offer a limited immersive experience for users
- may be susceptible to banner blindness
What is it about targeting options for connected tv ads?
When TV came to digital, magic happened. Connected TV ads give the opportunity to combine the best of TV — quality content, the largest most-trusted screen, and engaging storytelling environment — with the best of digital advertising — cross-platform identity stack powering relevant audience targeting.
In saying that, advertisers get the opportunity to precisely target their target audiences in different parameters using demographic targeting, OTT/Channel targeting, contextual targeting and so on. Also, brands can use retargeting and use first party data to connect with users.

How to measure Connected TV ad performance?
Measurement plays a vital role in media planning, buying, optimization and results of ad campaigns. Analytics and measurement of ad campaigns help to understand what is going on with ad campaigns and what needs to be improved. CTV advertising measurement is a hot topic nowadays and their KPIs brands should pay attention to measuring CTD ads performance:
- Impressions
- Reach
- Views
- Frequency
- View-through-rate
- Video completion rate
- CPM
Benefits of advertising on Connected TV
- Rich targeting options. Companies can easily reach the most relevant consumers with many targeting options by using the best and most engaging video formats and increasing the number of views for each ad.
- 100% visibility. Of course, video ads, unlike TV ads, can be skipped by clicking on the cross. But this task is not the easiest one, since if the user is watching content on the TV, they’d have to click on the cross in the right corner using the remote control. And since targeting advertising meets the audience’s interests, the desire to skip advertising is much less.
- Deep Data Analysis. CTV and OTT ads have more accurate tracking and many measurement options. Advertisers can use software platforms to collect and analyze all kinds of statistics and data to measure each ad campaign’s exact outcome. Advertisers can show metrics on the perfect ad side, such as ad completion rates and the viewers’ actions after viewing ads, such as website visits and conversions. It helps improve the quality of advertisements in the future and optimize them in the present and test new creatives.
- Help boost sales. 45% of Zoomers are regularly purchasing on their smartphones while watching streaming TV content. So brands no longer need to place ads everywhere in front of users to hopefully generate conversions — they can display ads on a big TV screen at the right moment, motivate users with a clear CTA to immediate action and increase revenue.
How to start with CTV advertising efficiently?
Start with programmatic (learn more about programmatic here). Artificial Intelligence is ruling the advertising world, and CTV is no exception. It has taken traditional methods of reaching users and optimized in real time them to be more efficient, personalized, relevant, and cost-effective. With programmatic advertising brands get the opportunity not to display their ads for everyone to see but show it only for valuable target users at the right moment and in the right place — even in TV campaigns.
For over 10 years, NT Technology has been helping brands reach customers and increase revenue with programmatic solutions. Our solutions for programmatic CTV ads help brands reach their target audience and high-intent users among them, wherever they are watching. And we are able to find audiences around the world driving reach and conversions with precise targeting, real-time optimization, custom audience segments, fraud protection, and multiple ad formats.
Advantages of Connected TV ad campaigns with NT:
- Quality Ad Inventory. Launch ad campaigns across major networks and streaming platforms around the world.
- Advanced Targeting. We deliver industry leading targeting options to find high-intent users for brands wherever they are.
- Dedicated Support. Our highly-experienced team have expertise across account management, strategy, Data Science, and Ad Operations and are ready to drive ongoing innovation and performance on your campaigns.
- Real-time optimization. We optimize ad campaigns across different KPIs to achieve results faster and with better price.
Make sure to see how programmatic advertising works on a real example of an ad campaign of our client.
How to increase awareness of car brand by 32.2% with programmatic Connected TV advertising
We launched the upper funnel ad campaign with connected TV to reach the target audiences on big screens with in-stream video. Video ads were shown on a mix of premium networks and channels, delivering predominantly on CTV. Additionally, we use a mix of channels on desktop and mobile devices to ensure outreach of the ad campaign.
We implemented a Brand Lift study to measure the impact of the client’s campaign. As a direct result of launching the ad campaign, we got a 32.2% increase in brand awareness.
Conclusion
The prospects for CTV advertising are broad and limitless. Get ready for the age of CTV with NT Technology. Reach out to us today to get strong results and drive profit tomorrow: click here to fill in the form or email us by info@nt.technology.
Read also